For continuous. stable ECG monitoring, not disturbed by the patient’s movement. How to measure ECG or EKG test with electrodes put on the patient’s chest. The following section describes various modified ecg 12 lead placement, which is similar to the standard 12 ECG leads.
Here you can know how to measure ECG
An EKG test is also called as the Electrocardiogram (ECG) test. Term EKG used in different locations of the world in use means the same medical term.
Some times EKG test confuses the student’s from healthcare professionals and patients
Try this The ECG Made Easy
Position Symbol Lead color
5 Lead electrode
Right intra-clavicular fossa R Red
Left intra-clavicular fossa L Yellow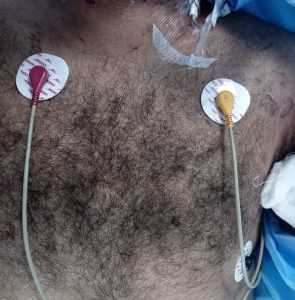
Left midclavicular line about 12-15 mm above the iliac crest or the left edge of the backbone about 12-15 mm above the iliac crest.
F Green
The right midclavicular line at the same level as F N (RF) Black
Any of the chest electrode positions C White
ECG Electrode Placement (5 Lead)
Chest electrode positions
C1 (V1): Fourth intercostal space at the right border of the sternum
C2 (V2): Fourth intercostal space at the left border of the sternum
C3(V3): Halfway between 02 (V2) and C4 (V4)
C4 (V4): Fifth intercostal space of the left midclavicular line
05 (V5): Left anterior axillary line at the same level as C4 (V4).
06 (V6): Left midaxillary at the same level as C4 (V4).
How to use ECG: Special Consideration
Place the electrodes on the patient before the electrode cable plugged into the monitor.
Special consideration should be given to electrode placement when using an electrosurgical unit. The active electrodes should be equidistant from the proposed cutting line but situated as far away as possible.
Care should be taken to ensure that the diathermy return plate is clean and makes good contact with the patient.
Though spikes observed in the ECG trace when using diathermy on the patient, instantaneous recovery of the ECG trace when diathermy electrodes removed from the patient.
Always ensure ECG cables are neatly dressed to avoid which may cause interference signals resembling cardiac waveforms on the EKG test monitor.
Poor ECG trace can occur due to dry electrodes. To rectify, remove the electrodes. apply the gel and re-attach with new tape. (Replace in case of disposable electrodes)
This monitor meets the safety requirements for direct cardiac monitoring.
The BOok for you
Read about Respiration assessment in Patients
Electrode Placement (3 Lead)
Right intra-clavicular fossa R Red
Left intra-clavicular fossa. L Yellow
Between 6th and 7th intercostal space on the left midclavicular line N Black
Lead connections (3 Lead)
Steps for application of ECG electrodes :
Proper skin preparation is necessary for the good quality signal to pick up and display. Please follow the guidelines listed below:
Wash electrode site and shave surface hair.
Gently rub skin surface with a prep pad to remove outer epidermal layer
Thoroughly clean the site with soap and water, depending on your patient’s skin type and sensitivity.
How to use ECG & application of ECG Electrode
Allow the site to dry thoroughly.
Check the expiry date on the electrode package. Ensure that the electrode gel is fresh before placing the electrode on the patient.
Use one electrode brand for all electrodes placed on a single patient. Mixing electrode brands may cause a fuzzy baseline or a lead fault message.
ECG leads the placement of an electrode on a flat. non-muscular area to avoid motion artifact.
How to measure ECG 12 lead placement?
Apply the electrode in the recommended way and print or record the ECG Trace in ECG paper roll given by the manufacturer
Procedure for applying the electrodes may vary with the type of electrode:
Wet gel type-press down along the edge of the electrode so that all edges adhere firmly to the skin. Do not press the central contact area of the electrode.
Solid gel type-begin by pressing on the gelled area. Then apply pressure toward the outside of the electrode.
Replace the electrodes at least every 48 hours.
Reusable ECG electrodes can be applied after applying a little bit of ECG gel on the cup of the electrodes & then securing the electrode at a site using sticking tape or suitable adhesive tape.
Fasten the electrode leads with surgical tape (with an extra length of wire between the tape and the electrode).
ln operation theatres. please ensure that the disinfecting cleaning solutions do not come in contact with ECG electrodes.
Clinical Limitations :
Shivering patients or patients giving exceptionally low signals can be difficult to monitor.
In spite of the fact that the screen is furnished with extraordinarily great channels against the impacts of electro-medical procedure. this method can influence waveforms and readings.
Defibrillation causes temporary disruption of the waveform display.
Patients with burns may need special needle electrodes.
Cardiac arrhythmias and pacemaker pulses can cause variation in heart rate
Caution
To ensure defibrillator and diathermy protection, use only L&T approved cables.
Warning
Pacemaker patients:
Rate meter may keep on checking the pacemaker rate during the event of heart failure or some arrhythmia. Do not rely entirely upon rate meter alarm to keep pacemaker patients under close surveillance.
3 lead / 5 lead ECG options for monitoring ECG. L&T offers either of these cables:
3 lead ECG cable (I, II, Ill)
5 lead ECG cable (I, ll, III, AVR, AVL, AVF, V1)
ST-Segment Analysis of EKG Test
ST portion demonstrates rise and sadness of ST section from ISO electric gauge which mirrors the essential data of patient’s heart work for myocardial ischemia (for example unevenness between oxygen supply and necessity in the myocardium)
Deviation or ST rise all the more then 1.0mm requires quick restorative consideration.
Why ST-segment analysis only?
ST-segment is the phase between the ventricular contraction (depolarization) and relaxation (repolarization).
Flow in coronary arteries occurs mainly in diastole, when the ventricular muscles are relaxing (repolarization). If the oxygen delivery is not sufficient. it may result in myocardial ischemia.
Read more about How to Measure ECG?

Why Multi-Lead ST monitoring?
Simultaneous processing of signals from 3 channels of ECG provides a multidimensional view of cardiac function, detecting changes that may not be visible in a single lead. Continuous monitoring is ensured, namely one of the leads is noisy. For a better analysis of use ECG 12 lead electrode.
ST analysis with 3 lead ECG cable
3 Lead ST-segment analysis will display the analysis of any one of the selected leads out of three (I, II, III).
Lead II gives maximum information, in the same way, it is preferred.
ST analysis with ECG 12 lead
Simultaneously any three selected Leads can analyze opt from seven (I, II, III. aVR, aVF, aVL, V). ECG leads placement in this test may vary from 3 electrode
Lead II and V give maximum information, lead II and V preferred.
ISO point
It is ISO electric point that provides the baseline for the measurement. By default ISO electric point is -82.5ms from R peak.
ST point
ST point is the measurement point where ST analysis is required. By default, the ST point measured at 97.5ms from the R peak.
Note: ST readings will be more accurate at diagnostic filter mode.