Surgical drain used for the drainage of the fluid residual and bleeding from the closed wound. Different types of drains are explained here.
- Corrugated drain
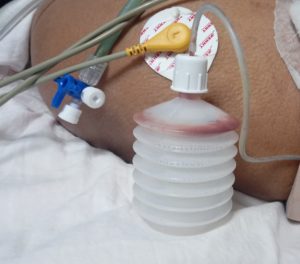
- Negative pressure suction bag (Romo-vac)
- Chest Drains
- Jackson Pratt drain
- Sump suction drainage
- Pigtail drain tube
- CBD T Tube
- Malecot’s catheter
- Redivac drain
- Malecot tube drain
Corrugated Drain
Drain made of the red rubber/ plastic or polyurethane. The drain has a groove on the surface of the drain, that helps in the drainage of the fluid and bleeding. This only drain that helps in the drainage of the fluids and bleeding from the surgical site of its own. It is cheaper than other tubes.
The duration of the drain in the surgical wound is about 3- 4 days of the operation.
It used in such a surgical operation like thyroidectomy, gastrectomy, cholecystectomy, some of the perineal abscess.
Complication
Fluid drainage from the wound can’t estimate.
The infection rate high when compared to other closed drains.
vacuum failure
Chest Drains
Chest drains mainly used in the cardiac and thoracic surgery, the chest drain applied for the collection of fluids from the fluids. The chest tubes made of the heavy Silastic material or polyvinyl chloride product.
Indication
closed chest drain
Pleural effusion and pneumothorax.
Emphysema
Cardiac surgery
Video-assisted Thoracotomy surgery VATS
Application
The chest tube is applied to the lateral of the chest by making a small incision in between the intercostal rings to reach the pleural cavity. Once it is reached the pleural cavity, the tube is connected to the under the water-seal chest drainage to remove the air, fluids from the thoracic cavity and pericardial cavity from the bronchus.
Assess the chest tube and the underwater seal chamber for the presence of fluctuation.
After the insertion, the chest drain tube is fixed with the Non-absorbable suture and dressing must be done with petroleum gauze or plain sterile gauze covering the tube insertion site.
Continuous monitoring of the under water-seal chest drain collection with the water level maintenance.
Complication
Pneumothorax.
Infection.
Uses of Surgical Drain
To eliminate dead space
To evacuate the vacuum, blood, fluids, bile juice.
According to the working principle
1.Active (example-corrugated drains)
2.Passive (example-Romo-vac), ICD
It uses the high-pressure suction and low-pressure vacuum.
Surgical drain Complication
Infection
Pain and discomfort
Blockage
Poor drain selection
Erosion of the tube with other internal organs.