Subcutaneous injections are a common medical procedure used to administer medications into the layer of tissue just beneath the skin. While seemingly straightforward, mastering the technique is crucial for healthcare professionals to ensure optimal patient care and comfort. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of subcutaneous injections, covering everything from the procedure itself to best practices for injection site selection and patient education.
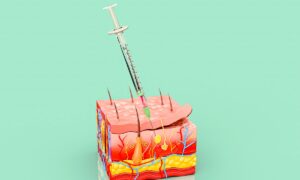
Understanding Subcutaneous Injections: Subcutaneous injections involve delivering medication into the subcutaneous tissue, which lies between the skin and the muscle layer. This route is often chosen for medications that require slow, sustained absorption into the bloodstream. Common medications administered via subcutaneous injection include insulin, certain vaccines, and some types of hormonal therapies.
Subcutaneous Injections Procedure
- Preparation: Begin by gathering the necessary supplies, including the medication vial, syringe, alcohol swab, and a sharps container for safe disposal of used needles.
- Patient Assessment: Assess the patient’s medical history, allergies, and current medications to ensure compatibility with the prescribed medication.
- Site Selection: Identify appropriate injection sites, typically areas with a layer of adipose tissue, such as the abdomen, upper arms, thighs, or buttocks.
- Preparation of Medication: Follow proper aseptic technique to draw the correct dose of medication into the syringe, ensuring accuracy and minimizing the risk of contamination.
- Injection Technique: Pinch the skin at the selected site to create a subcutaneous tissue fold. Insert the needle at a 45 to 90-degree angle, depending on the patient’s body habitus and the length of the needle. Administer the medication slowly and steadily.
- Post-Injection Care: Remove the needle gently and apply pressure to the injection site with a clean cotton ball or gauze pad to minimize bruising and bleeding. Dispose of the used needle and syringe in a designated sharps container.
Best Practices
- Rotate Injection Sites: To prevent tissue damage and ensure optimal medication absorption, rotate injection sites regularly.
- Educate Patients: Empower patients with knowledge about the importance of proper injection technique, site rotation, and potential side effects to enhance medication adherence and safety.
- Monitor for Adverse Reactions: Be vigilant for signs of allergic reactions, injection site reactions, or other adverse effects, and intervene promptly if necessary.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of subcutaneous injections is an essential skill for healthcare professionals across various clinical settings. By understanding the principles of proper technique, site selection, and patient education, healthcare providers can ensure the safe and effective administration of medications via this route, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes and quality of care.
Sharing is caring!