Endoscopic Third ventriculostomy procedure, a minimally invasive surgery done using a neuro endoscopy procedure for visualization and bypass Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) through the third ventricle of the brain.
Indication
Hydrocephalus due to obstruction
Pathological condition
Intraventricular cyst
Neurocysticercosis
Cyst or Tumours causes Hydrocephalus
Position
Make sure all the imaging facility and detailed notes of procedure written on the notice board of the Operating room
The patient placed in a supine position with a slight head flexed according to the site of the incision. Precoronal frontal burr hole 3 cm lateral to the midline.
Endoscopic ventriculostomy: Instrument used
- Complete Endoscopy Console
- Camera
- Light cable
- Irrigation system [warm RL Solution]
- Endoscope holder or Leyla arms (two) attached to the table
- Trocar and sheath
- O Ventriculoscope
- Operative endoscope
- Bipolar endo-surgical unit with the appropriate accessory
- Fogarty balloon catheter
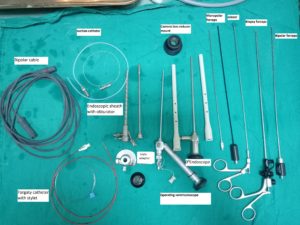
- Biopsy forceps
- Endoscopic scissor
Craniotomy: Burr hole
- #20 with BP handle blade for skin incision
- #15 blade for dura mater
- Tissue holding forceps
- Drill (Electric or Pneumatic) or Hudson brace for Burr hole
- Periosteal elevator
- Irrigation syringe with saline
- Dural Scissor
- Bayonet forceps
Before they start painting the patients with the disinfection solution. Surgical site cleaning and drape the patient exposing the surgical site. Mark the incision site on the head, and create a flap on the incision site.
Note: In some cases Stereotactic method used for accuracy. (Neuro navigation assisted)
For holding the endoscope using the endoscopic holder or Leyla retracting system. The surgeon may choose the flexible endoscopic holding system for the usage, according to their concern
After opening the skull with Hudson brace burr or electric Drill/Pneumatic drill, open the dura mater with the #11 blade.
In some of the cases, the surgeon and anaesthesiologist check the intracranial pressure.
ETV endoscopic third ventriculostomy procedure
After the insertion of the brain cannula connected to the ICP transducer, ICP monitored and documented for future reference.
Insert the brain cannula for the CSF drainage and collect CSF for analysis and then insert the trocar with a sheath to enter the ventricle. Remove trocar and insert 00Endoscope for visualization of the ventricle. Connect to the irrigation system (Warm Ringer lactate solution).
Connect the irrigation port to the endoscopic sheath for better visualization inside the brain

structure.
Insert operating endoscope and fix it to the sheath.
Enter the third ventricle through the foramen of Monro and fix the endoscope above the floor of the third ventricle.
In the third ventricle, mammillary bodies are identified as two white bulges and infundibular recess a
s orange structure. In between infundibulum and mammillary bodies the dorsum sell is seen as a white band like structure through the floor of the third ventricle. The basilar artery is seen through the floor between dorsum sellae and mammillary bodies. The floor of the third ventricle is perforated with forceps or bipolar electrodes without using energy between the dorsum sellae and basilar artery. The perforation is enlarged by the inflating Fogarty balloon (3F). The balloon using a Ringer lactate solution or air.
Inspection of the prepontine area to visualize the basilar artery in subarachnoid space. After continuous Ringer lactate saline irrigation to control hemostasis confirm that there is no damage to the foramen of Monro and withdraw the scope
Biopsy procedure
For the biopsy procedure, rotate the endoscope to 1800 Ventriculoscope for better visualization and to access the tumor in the posterior third ventricle. Biopsy sample store in the sample table with normal saline. Control hemostasis after biopsy, using Ringer lactate irrigation. If hemostasis not controlled, use a Bipolar endo-surgical unit or Fogarty catheter inflation inside the tumor.
Closure
#3-O Vicryl suture for galea
2-O Silk suture for skin closure
Needle holder
Thumb forceps
Anatomy of ventricle
Ventricles of the brain- a total of 4 ventricle
2 lateral ventricle (Right and left)
Third ventricle and fourth ventricle
Ventricles present in both sides of the cerebral hemisphere which communicates with each other. C-shaped lateral ventricles with frontal horn anterior
Posterior -Body, Atrium, Occipital horn
Inferior- Temporal horn
Ventricles with Fluid called CSF-Cerebro spinal fluid which secretes from choroid plexus.
Post reviewed and edited by Dr.Dhaval Shukla Professor of Neurosurgery, NIMHANS, Bangalore.